Difference between revisions of "ZKKP Pyongyang FIR"
(→China LOA and Meters) |
(→Japan LOA) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=== Japan LOA === | === Japan LOA === | ||
| + | Japan does not maintain any airway or route connections with Pyongyang FIR. Traffic routed to Japanese airspace shall follow airways connected via Khabarovsk FIR (north) or Incheon FIR (south). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Traffic enroute via Incheon FIR:<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''KANSU''' Z56 SABET L512 ANDOL | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Traffic enroute via Khabarovsk FIR:<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''NULAR''' B233 LURED B451 IGROD | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The reverse routes from Japanese airspace are expected as well. See Incheon and Khabarovsk LOA's for more information on coordinating with South Korean and Russian controllers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Off route direct is discouraged, but if essential for IVAO network operations, direct to '''EKVIK''' to join RNAV airway Y347 can be approved upon coordination with Japanese controllers. | ||
=== Russia LOA === | === Russia LOA === | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 31 October 2017
안녕하십니까 - Annyong Hashimnikka
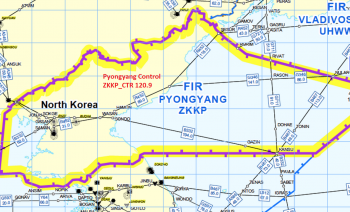
Welcome to the ZKKP Pyongyang Flight Information Region (FIR) wiki page for North Korea's airspace, part of the IVAO XE East Asia Region Division! These sets of pages should help provide you with all the information you need while controlling North Korean airspace.
Note: Please keep in mind, IVAO stresses that our network is at global peace without any conflicts between nations. We also strive to simulate realism. So, while it is ok to respect the prohibited airspace at the DMZ between the DPRK and ROK, on IVAO, direct flights are permissible between the two nations. At no time shall any war simulation be performed in Korean airspace as this is a huge violation against IVAO rules and regulations. That being said, enjoy Pyongyang Control
Contents
Airspace Overview
Pyongyang Control
Here are a list of the valid center positions IVAO XE authorizes in North Korean airspace.
All radio callsigns are "PYONGYANG CONTROL" regardless of sector.
| Sector Position | Callsign | Frequency | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyongyang Control | ZKKP_CTR | 120.900 | Primary, Above FL140 over Pyongyang and Kalma TCA's. Covers entire FIR when other positions offline |
En Route and Cruise
Phraseology
Due to the fact that resources and ATC recordings and feeds are non-existent for the DPRK, the IVAO XE division encourages use of standard ICAO phraseology when controlling Pyongyang Control.
RVSM Airspace
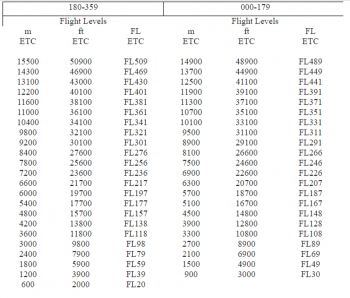
North Korea has switched a few years ago from meters to RVSM airspace from FL290-FL410, and as such follows standard semi-circular rules in feet (FL).
360-179 odd flight levels (ex. FL290, FL310, FL230)
180-359 even flight levels (ex. FL300, FL240, FL380)
However, aircraft departing the DPRK with a final destination in Russia, China, or Mongolia will be assigned a meter altitude from departure. Use the charts below in the LOA section to help determine a cruise meter altitude.
Transition Altitude
Transition Level is FL130. Transition Altitude is 12,000ft throughout the entire FIR.
North Korea uses QNH (standard 1013 hectopascals or millibars)
Transponder Codes
All transponder codes in North Korea range from 4001-4077
China LOA and Meters
Aircraft departing Pyongyang or Kalma to a Chinese destination can be assigned a meter altitude from departure.
All handoffs will go to Shenyang Control ZYSH_CTR:
VASRO - R224 RNAV airway
GOLOT - A345 RNAV airway and A575 airway
PONIL - B332 airway
Off route flying towards the quad-FIR border with Incheon, Shanghai, Shenyang, and Pyongyang is strictly forbidden. However, if traffic shall find their way at this point towards China, handoff to Shanghai ZSHA. If in contact, vector aircraft back towards the B332 airway and handoff to Shenyang.
All aircraft entering Chinese airspace must be assigned a meters altitude by Pyongyang control prior to initiating a handoff to Shenyang or Shanghai or sent to UNICOM. Use the chart below to match the nearest meters level to the flight level they are cruising at or filed in Korean airspace. For example, if they are cruising at FL360, assigned 11,000 meters which will translate to FL361/36,100ft. When an aircraft enters Korean airspace from China, assign a cruise flight level nearest to their meters level as Chinese controllers normally do not assign a FL prior to handing off to Korean controllers.
Japan LOA
Japan does not maintain any airway or route connections with Pyongyang FIR. Traffic routed to Japanese airspace shall follow airways connected via Khabarovsk FIR (north) or Incheon FIR (south).
Traffic enroute via Incheon FIR:
KANSU Z56 SABET L512 ANDOL
Traffic enroute via Khabarovsk FIR:
NULAR B233 LURED B451 IGROD
The reverse routes from Japanese airspace are expected as well. See Incheon and Khabarovsk LOA's for more information on coordinating with South Korean and Russian controllers.
Off route direct is discouraged, but if essential for IVAO network operations, direct to EKVIK to join RNAV airway Y347 can be approved upon coordination with Japanese controllers.
Russia LOA
Aircraft departing Pyongyang or Kalma to a Russian destination can be assigned a meter altitude from departure.
ADNUR - TO Russia on B356 airway
BUMEP - FROM Russia on B355 airway
RIVAT - A900 and G705 airways
NULAR - B941, A934, and B233 airways
All aircraft entering Russian airspace must be assigned a meters altitude by Pyongyang control prior to initiating a handoff to Khabarovsk or sent to UNICOM. Use the chart below to match the nearest meters level to the flight level they are cruising at or filed in Korean airspace. For example, if they are cruising at FL360, assigned 11,000 meters which will translate to FL361/36,100ft. When an aircraft enters Korean airspace from Russia, assign a cruise flight level nearest to their meters level as Russian controllers normally do not assign a FL prior to handing off to Korean controllers.
South Korea LOA
See RKRR Incheon FIR for more information on South Korean airspace.
Seoul Arrivals
Terminal Control Areas
under construction